[1/9/24]
Brushed DC Motor

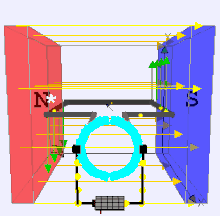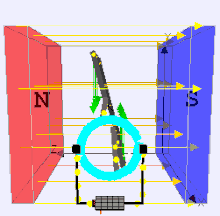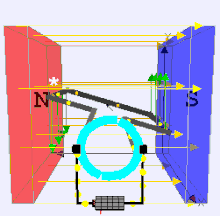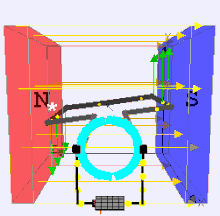
A Brushed DC (Direct Current) electric motor is a type of electric motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy using direct current and brushes to facilitate the commutation process. It is one of the simplest and oldest types of electric motors and is widely used in applications requiring variable speed and high torque.
Key Components:
- Stator: The stationary part of the motor, often containing permanent magnets or an electromagnet.
- Rotor (Armature): The rotating part that is connected to the output shaft.
- Commutator: A mechanical switch that reverses the direction of current in the rotor windings, ensuring continuous rotation.
- Brushes: Conductive materials (usually carbon) that maintain electrical contact between the stationary circuit and the rotating commutator.
Working Principle:
The brushed DC motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field experiences a force. The brushes and commutator work together to change the direction of current in the armature windings, ensuring that the force generated is always in the same direction relative to the magnetic field, producing continuous rotation.
Types:
- Shunt Motor: The field windings are connected in parallel with the armature.
- Series Motor: The field windings are connected in series with the armature.
- Compound Motor: Combines characteristics of both shunt and series motors.
Advantages:
- Simple design and construction.
- High starting torque.
- Easy to control speed and direction.
- Cost-effective for many applications.
Disadvantages:
- Brushes and commutator require maintenance.
- Limited lifespan due to wear and tear of brushes.
- Can generate electrical noise due to brush contact.
[3/23/25]